Lab5
Last modified: 11/27/2024 7:40:00 PM
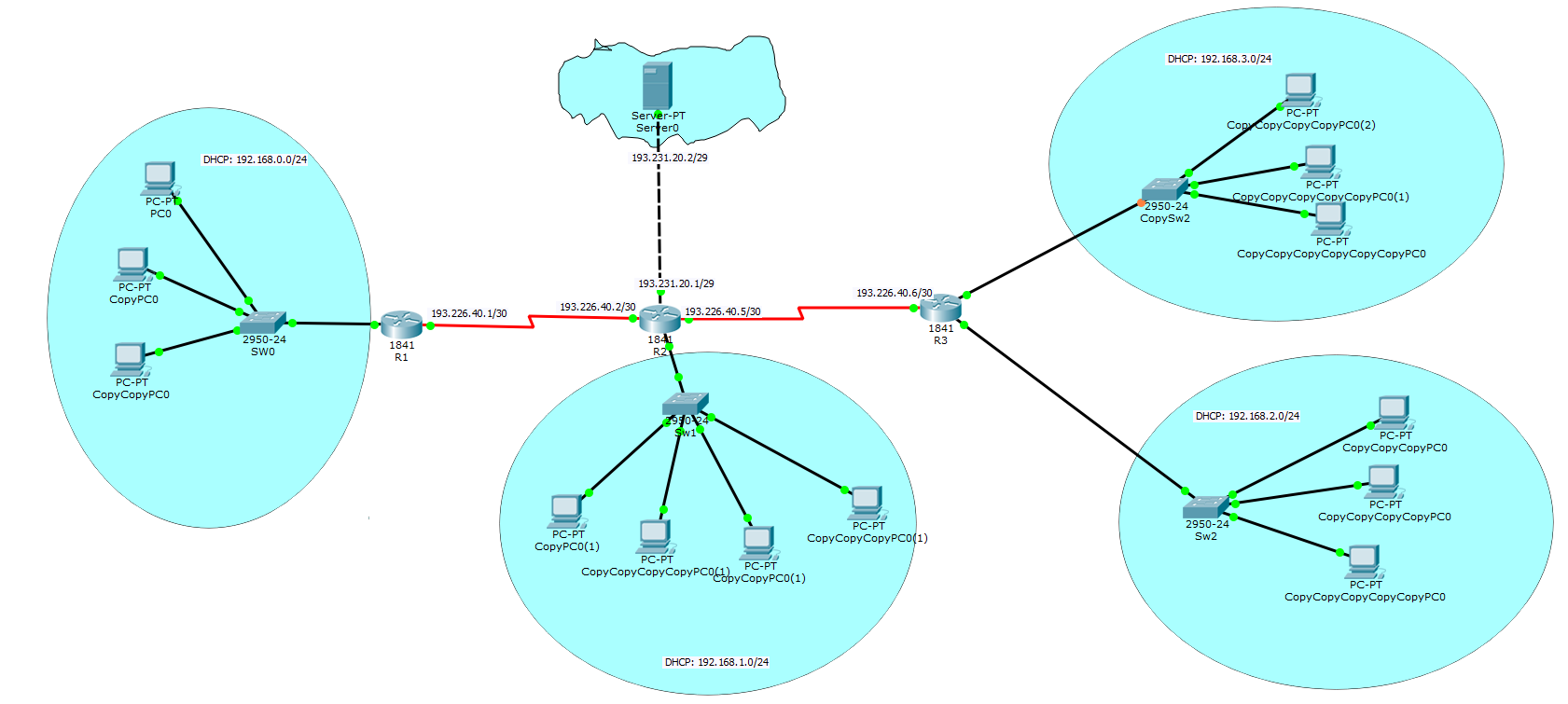
Use Packet Tracer to
create a network topology like the one bellow and setup IP Addressing and
manual routes such that:
·
All
local LAN PCs have
intra-lan access to each other (ping)
·
Setup
routing such that LAN 192.168.2.0/24 and 192.168.3.0/24 could access each
other. Do you need to do anything?
·
Setup
NAT access from all networks to the server in Internet (193.231.20.2) such that
its web server is accessible from all LANs
·
Setup
physical locations for all equipment such that
o
192.168.0.0
is in city Cluj Napoca, building UPC (at least 1km
away from FSEGA and UBBMainBuilding)
o
192.168.1.0
is in city Bucharest, building ROEDU (at least 1km away from other buildings in
Bucharest)
o
192.168.2.0
is in city Cluj Napoca, building FSEGA (at least 1km
away from other building in Cluj Napoca)
o
192.168.3.0
is in city Cluj Napoca, UBBMainBuilding
(at least 1km away from other building in Cluj Napoca)
o
193.231.20.2
is in city Bucharest, building Google (at least 1km away from other buildings
in Bucharest)
The links between
R1-R2-R3 are serial links. You need to add serial interfaces to those 1841
Routers as they are not equipped with. There is no special setup for serial
links otherwise. Just IP addressing.
Requirements:
1. Be able to access the
Internet Server 193.231.20.2 from all networks (NAT)
2. Be able to access
networks 192.168.2.0 and 192.168.3.0 from each other
3. What happens with
network access between private nets 192.168.0.0 and 192.168.1.0.
4. What happens with
network access between private nets 192.168.x.0 ? Can
this be solved ?
You will need to
familiarize yourself with the following procedures for solving the problem:
1. Router CLI interface
and commands for setting up:
a. Enter admin mode in a
router CLI (enable)
b. Enter configuration
mode in router CLI (config terminal or
conf t)
c. Manage Static routes (in configure mode – ip
route ….)
d. DHCP pools for local
LANs (in configure mode – ip dhcp pool ….)
e. NAT setup ( in configure mode ip
nat inside/outside , etc)
f. Show configuration (enable or just at prompt – show ….)
Notes:
Router Configuration
For any equipment configuration try to setup things in the config tab and watch the equivalent commands as you should have enter them in order to accomplish the same task in the bottom side of the window. There are things that cannot be configured from the graphical user interface. In order to learn new commands try the help system “?”. After any part of a command entered, placing a “?” shows the remaining parameters and their explanation. Usually a user needs administrative privileges (or entering privileged mode) in order to apply any new configuration changes to a router. The command to enter privileged mode is enable.
From privileged mode – most of configuration changes need a special mode that is entered by using the command:
config t – as configure terminal – which enters configuration mode. You need to type CTRL+Z or exit .
In order to make router settings changes permanent one needs to copy the current running configuration into the startup configuration. The command to accomplish this is copy running-config startup-config. Upon reboot the router will keep its configuration.
DHCP – configuration
In order to configure a DCHP service on a router you need to setup a dhcp pool, define its range and parameters and excluded IPs. The necessary commands are (from config mode):
#define a dhcp pool of addresses to be delivered
ip dhcp pool <name_of_pool>
Ex: ip dhcp pool lan
#define the network range
network 192.168.0.0
255.255.255.0
#define the default gateway (if any) that should be passed to the clients
default-router
192.168.0.1
#define the DNS server (if any) that should be passed to the clients
dns-server 192.168.0.3
#exit dhcp pool configuration
exit
# If there any IPs in that range that you do not want to be served to PCs - add them to the excluded range:
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.0.1 (for a single IP)
#or
ip dhcp excluded–address 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.10 (for a range of IPs)
NAT configuration
In order to config NAT on a router on needs to specify one or multiple inside (local LAN) interfaces and one or multiple outside (WAN) interfaces. After setting
up NAT all packets travelling from an inside interface to an outside
interface are NAT-ted (their IP addresses are changed
according to the NAT policy in place).
Suppose in our case that FastEthernet 0/0 (192.168.0.0/24 range) is inside and Serial 0/0/0 (193.226.40.1) is outside.
In order to accomplish NAT we do the following:
Router:
enable
conf t
interface FastEthernet 0/0
#specify that this is an inside interface. The interface needs to have an IP Address
ip nat inside
exit
#define Serial 0/0/0 as WAN (outside) interface
interface Serial
0/0/0
ip nat outside
exit
Define an Access list with the addresses from the inside that can be nat-ted. The 0.0.0.31 specify the masks of bits from the IP Address that can vary. In our example bellow all addresses between 192.168.0.1 – 192.168.0.31 would pass !
# thease are simple one liner lists
access-list 1 permit
192.168.0.1 0.0.0.31
#or
extended lists that are defined as lists of rules – these allow the actions
where they are going to be applied from source (192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 -equiv to 192.168.0.0/24 to destination 193.231.20.0/24)
ip access-list
extended nat-internet
permit ip
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255 193.231.20.0 0.0.0.255
permit ip
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 193.231.20.0 0.0.0.255
permit ip
192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 193.231.20.0 0.0.0.255
permit ip
192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 193.231.20.0 0.0.0.255
#define a pool of addresses to be allocated to the clients when NAT-ted. First IP – last IP netmask for those IPs
ip nat pool ISP 193.226.40.1
193.226.40.1 netmask 255.255.255.252
Define the NAT policy. The NAT policy applies NAT by selecting a source and a NAT pool or single IP (which replace the private range)
Overload allows to use a single outside IP from the defined pool for multiple clients – by altering the port. One port is allocated on that IP for each outgoing client. Overload allows this behavior.
ip nat inside
source list 1 pool ISP overload
or
#choose an interface
that will provide the public IP and you do not need to define a pool !:
ip nat inside source list
1 interface Serial0/1/1 overload